
The market for Android applications is huge, and in 2022, Google Play users worldwide downloaded 111.3 billion mobile applications. There is no denying that vulnerabilities in the android applications could affect a lot of people negatively. That is why there is a need for security tests on Android applications is important.
Android is an operating system that is widely used for mobile or smartphones. The development of Android can be said to be very fast so that a lot of updates from the previous operating system version. Android has applications that are used to do various things, such as word or data processing, image processing, sound processing, video processing, and various other application features. The application was developed using Java and Kotlin programming languages. The Kotlin programming language is a new, more practical programming language.
However, at this time many developers have developed a framework for the creation and development of other mobile applications, both Android and IOS. The framework was developed using various programming languages and various technologies. Examples of such frameworks are React Native, Flutter, and Kivy. The rapid development of the Android operating system resulted in this operating system being widely used for mobile or smartphone platforms. This development ultimately makes the application that comes from the developer only concerned with the function without regard to the security of the application.
OWASP
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit foundation dedicated to improving software security. It operates under an “open community” model, which means that anyone can participate in and contribute to OWASP-related online chats, projects, and more. For everything from online tools and videos to forums and events, the OWASP ensures that its offerings remain free and easily accessible through its website.
The OWASP Top 10 provides rankings of—and remediation guidance for—the top 10 most critical web application security risks. Leveraging the extensive knowledge and experience of the OWASP’s open community contributors, the report is based on a consensus among security experts from around the world. Risks are ranked according to the frequency of discovered security defects, the severity of the uncovered vulnerabilities, and the magnitude of their potential impacts. The purpose of the report is to offer developers and web application security professionals insight into the most prevalent security risks so that they may fold the report’s findings and recommendations into their own security practices, thereby minimizing the presence of known risks in their applications.
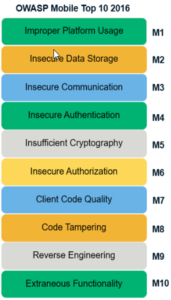
The OWASP Mobile Top 10 at a Glance
The OWASP Mobile Top 10 give you an overview of the ten most critical security risks to your apps and web applications. They show you which attack vectors to expect and how to protect against them.
-
Improper Platform Usage
The first item among the OWASP top 10 is improper platform usage. Platforms such as iOS, Android, or Windows Phone provide different capabilities and features that you can use. If the app does not use an existing function or even uses it incorrectly, this is called improper use. This can be, for example, a violation of published guidelines that affects the security of the app. Unlike the other items in the OWASP Mobile Top Ten, this aspect is not aimed exclusively at app developers. The problem with violating common conventions is that it allows for unintended misuse.
-
Insecure Data Storage
Insecure data storage, as well as unintentional data leaks, also fall under the OWASP Mobile Top Ten. Mobile application penetration testing tools help uncover such grievances. However, it does not necessarily have to be your SQL database. Manifest and log files, cookie storage or cloud synchronization can also be affected. By the way, this problem occurs so often that it should be an important part of your OWASP Mobile Security Checklist. The reason is almost always found in insufficiently documented or undocumented internal processes.
-
Insecure Communication
Your app transports data from point A to point B. If this transport is insecure, the risk increases. Here, too, the main mobile application penetration testing tools will help you. They support you in detecting faulty app-to-server or mobile-to-mobile communication. The biggest problem is the transfer of sensitive data from one device to another. This could be encryption, passwords, account details or private user information. If the necessary security measures are missing at this point, it is easy for hackers to access your data.
-
Insecure Authentication
Secure authentication adds another key security aspect to your OWASP Mobile Security Checklist. In fact, there are many different ways that the app can provide insecure authentication. A classic example is a back-end API service request that the mobile app executes anonymously without relying on an access token. Additionally, there are still apps that store passwords locally in clear text. To mitigate these potential risks, consider OWASP’s recommendations.
-
Lack of Cryptography
The insecure use of cryptography can be observed in most app applications. This is almost always one of two problems: a fundamentally flawed process behind the encryption mechanisms or the implementation of a weak algorithm.
-
Insecure Authorization
Unlike authentication, authorization deals with the verification of an identified person. It verifies that the necessary authorizations are in place to perform certain actions. Of course, the two are closely related – yet both items belong separately on the OWASP Top 10 list. Both are mutually dependent, which is why a lack of authentication almost always leads to a lack of authorization. You need to secure these vulnerabilities as soon as possible to protect your sensitive corporate data from unwanted access.
-
Poor Client Code Quality
This item of the OWASP Top 10 refers to an explicit programming language. All vulnerabilities from code-level errors can provide attackers with a way inside. The main risk lies in the need to make localized changes to the code. In particular, insecure API usage or insecure language constructs are common problems that you need to fix directly at the code level.
-
Code Manipulation
From a technical perspective, any code on a mobile device is vulnerable to tampering. This is because the mobile code is running in a foreign environment. It is no longer under the control of your organization. Therefore, there are numerous ways to modify it at will. You should always consider these unauthorized changes in the context of business implications.
-
Reverse Engineering
Attackers who want to understand how your app works can use reverse engineering to access all the information they need. Especially metadata, which is supposed to be a relief for your programmers, is a high risk. Basically, if you can clearly understand the string table of the binary or cross-functional analysis is possible, the app is considered at risk.
-
Extraneous Functionality
Hidden backdoor functionality or internal security controls are a common problem in mobile applications. The problem with them is that they are not only useful for developers, but also for hackers. This allows them, for example, to disable 2-factor authentication or change basic functionality.
