In the past, Candida infections were only recorded in people with a compromised immune system. However, cases of Candida have been on the rise in recent years, with a lot more people reporting symptoms. In this article, we will look at what you need to know about Candida, how to recognise an infection, and what to do if you have an infection.
What is Candida?
Candida is a type of yeast found in the body, typically in the digestive tract and reproductive systems. The presence of this type of yeast is typically not a problem. It becomes one when there is a yeast or Candida overgrowth. It is this overgrowth that causes a Candida infection and symptoms.
What Causes a Candida Overgrowth?
Overgrowth typically happens when there is an imbalance in the digestive tract in other parts of the body. This imbalance can be caused by an overuse of antibiotics that kill the bacteria that keep Candida in check, overconsumption of alcohol, and a poor diet.
Other causes include the use of birth control pills and oestrogen replacement therapy, high chronic stress levels, recreational drug use, and chemotherapy.
Candida Symptoms
Typical symptoms of Candida include:
- Loose stool
- Constipation
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Panic attacks
- Insomnia
- Excessive gas
- Chronic fatigue
- Stomach distension
- Low sex drive
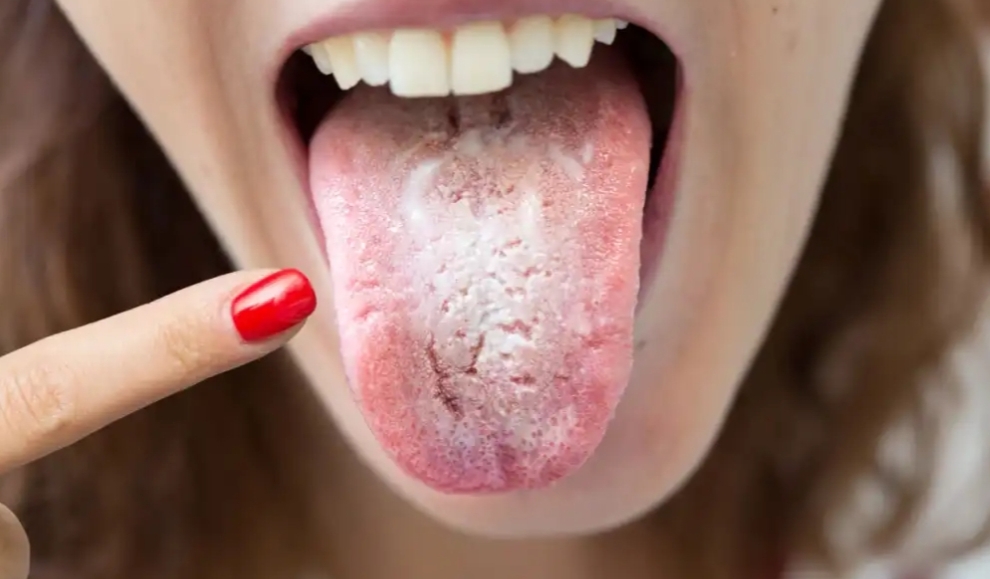
- White tongue
- Brain fog
If you have any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor so they can perform a Candida test. If you test positive, they will propose treatments and other interventions.
Candida Treatment
Because Candida infections and symptoms are due to its overgrowth, the most common intervention is limiting yeast production and killing off the Candida in the body.
The aim is to bring the yeast levels down and to ensure they return to normal levels. The treatment for Candida starts with specific anti-fungal supplements, prebiotics and probiotics.
They will also advise you on the dietary changes you should make to reduce the overgrowth. Diet plays a significant part in Candida infections, so the doctor will also ask you to limit dietary products, processed foods, alcohol, refined carbohydrates and refined sugars.
However, everyone’s case and the cause of their infection differ, so the doctors only advise these restrictions and changes after a thorough assessment.
Lastly, the doctor will recommend that you stop taking medications causing the infection or making it worse. This includes broad-spectrum antibiotics and corticosteroids.
If you need these medications, the doctor might substitute them. However, never stop taking any medication unless a doctor advises you to.
Can You Spread Candida?
Candida is fairly difficult to spread from one person to another. However, it is possible. If the infection turns into a yeast infection, it is possible to pass it to a partner during sex.
Candida is a yeast that lives inside and outside the body. Typical levels of Candida do not cause an infection or symptoms, but overgrowth can lead to serious issues and complications. This happens when the bacteria that keep Candida infections under control is somehow compromised.
The good news is we now understand Candida much better than we did a few decades ago, and treatments have become more readily available.
